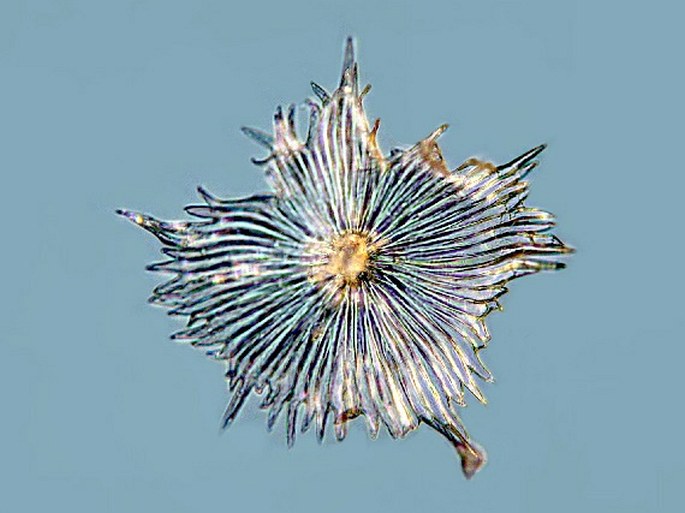

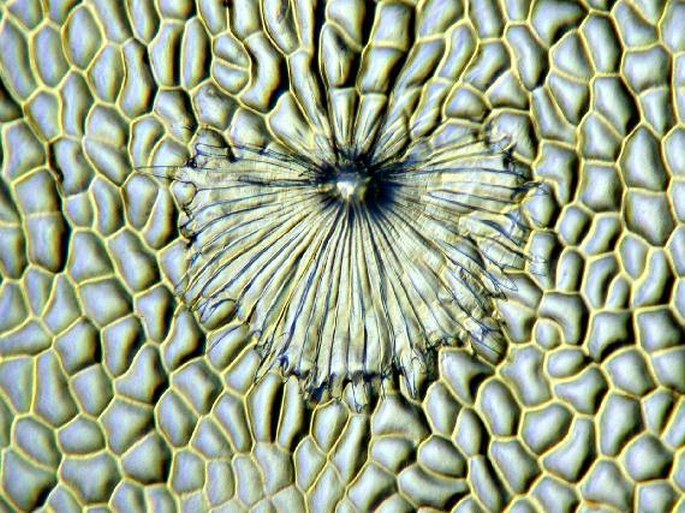

The surface of the leaves of the Olea europaea, Elaeagnus commutata or Hippophae rhamnoides is covered by numerous stellate hairs – trichomes. They are well apparent in the reflected light (at the top), in a microrelief (in the middle) or in the transmitted light (down). Photomicrograph, prim. magn. 30–100×.

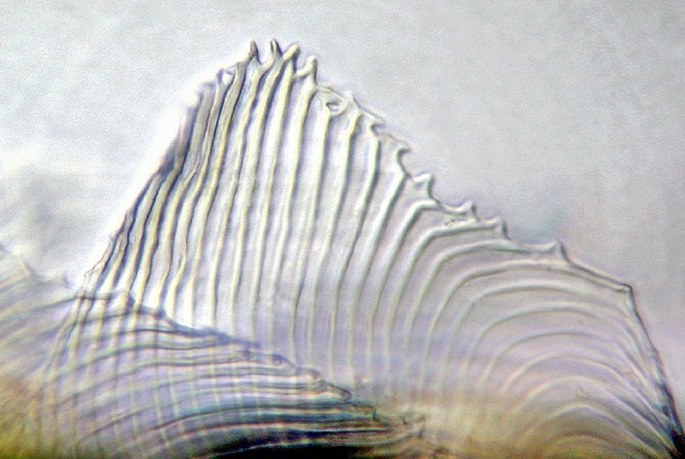
Tillandsia (Tillandsia sp.) is covered by a peltate trichomes which collect a moisture. Photomicrograph of the detail (down), prim. magn. 400×.
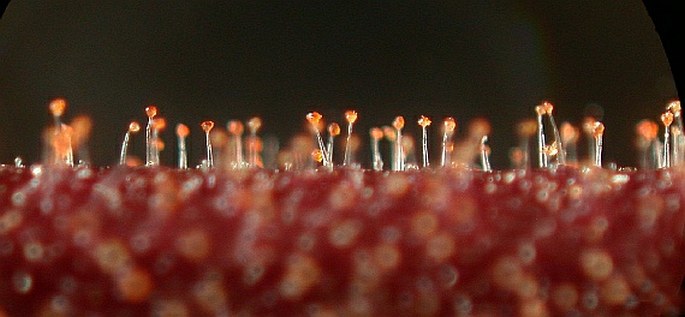

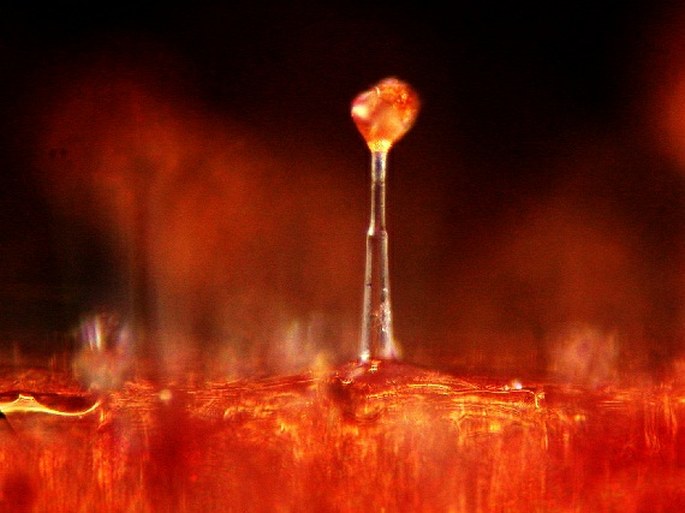
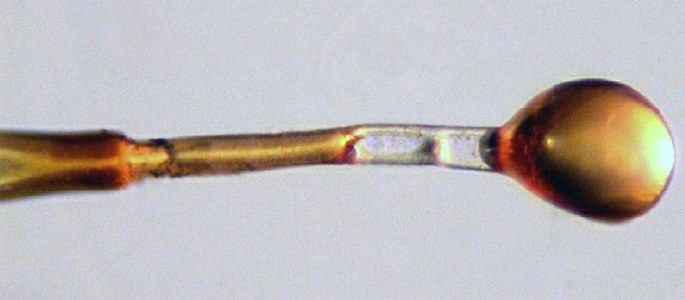
Glandular trichomes of the Pelargonium with their spherical secretory tips. Photomicrograph, prim. magn. 30–400×.

A needle-like trichome of an Urtica (Urtica dioica).
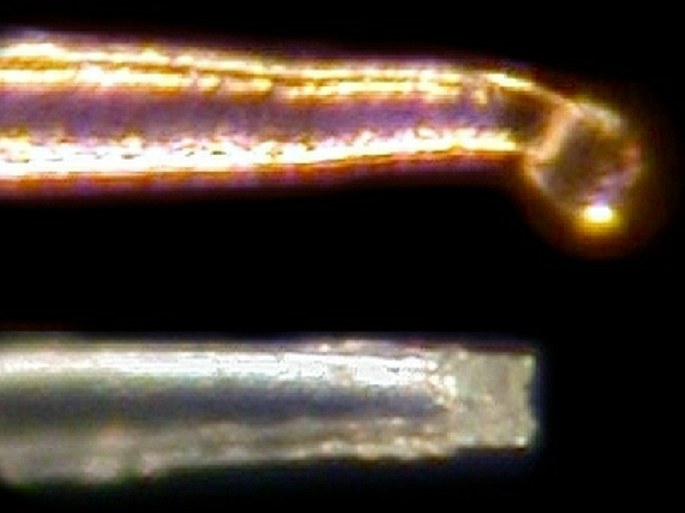
A stinging trichome of the Urtica (Urtica dioica). Its silicic tip breaks after an impact like an injection vial and, from the hollow hair, an acidic content is injected into the skin. Photomicrograph, prim. magn. 400×.
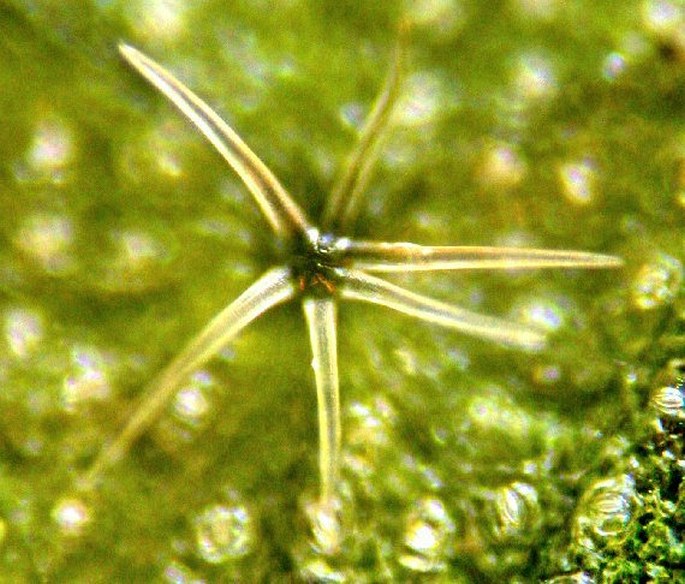

A radial trichome of the Hibiscus in the reflected light. Photomicrograph, prim. magn. 100×.
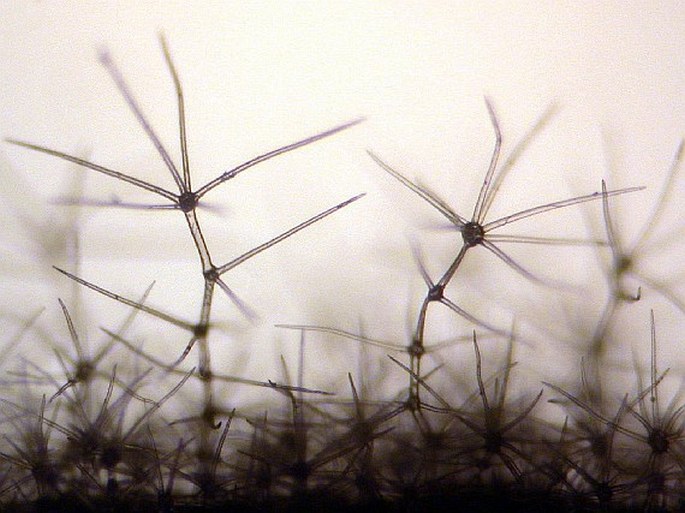

Branched trichomes of the Verbascum. Photomicrograph, prim. magn. 100×.
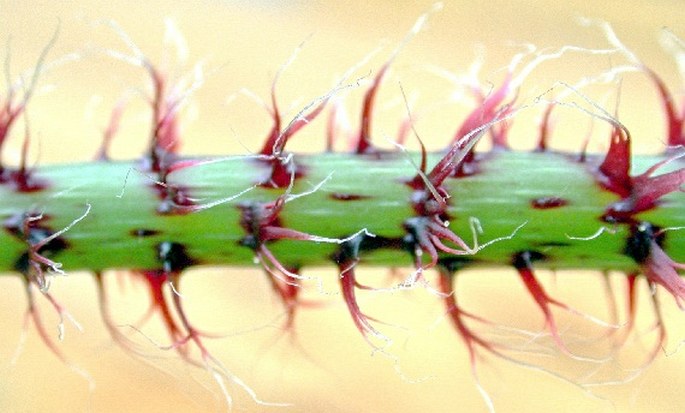
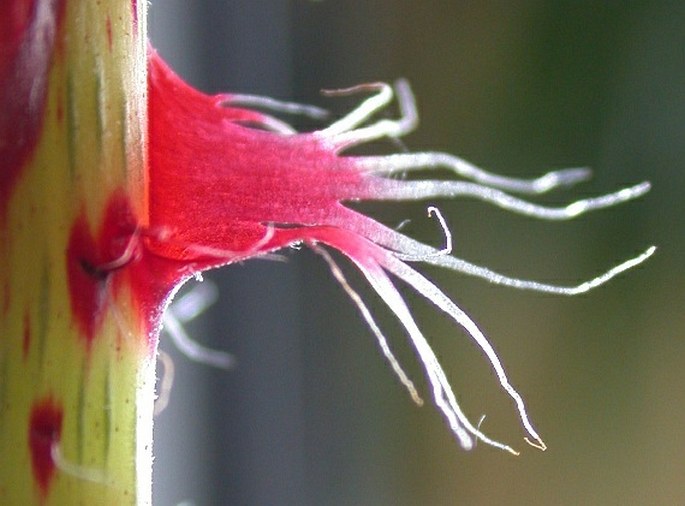


Multicellular trichomes on the Begonia petiole.


